TECHNOLOGY
theranostics
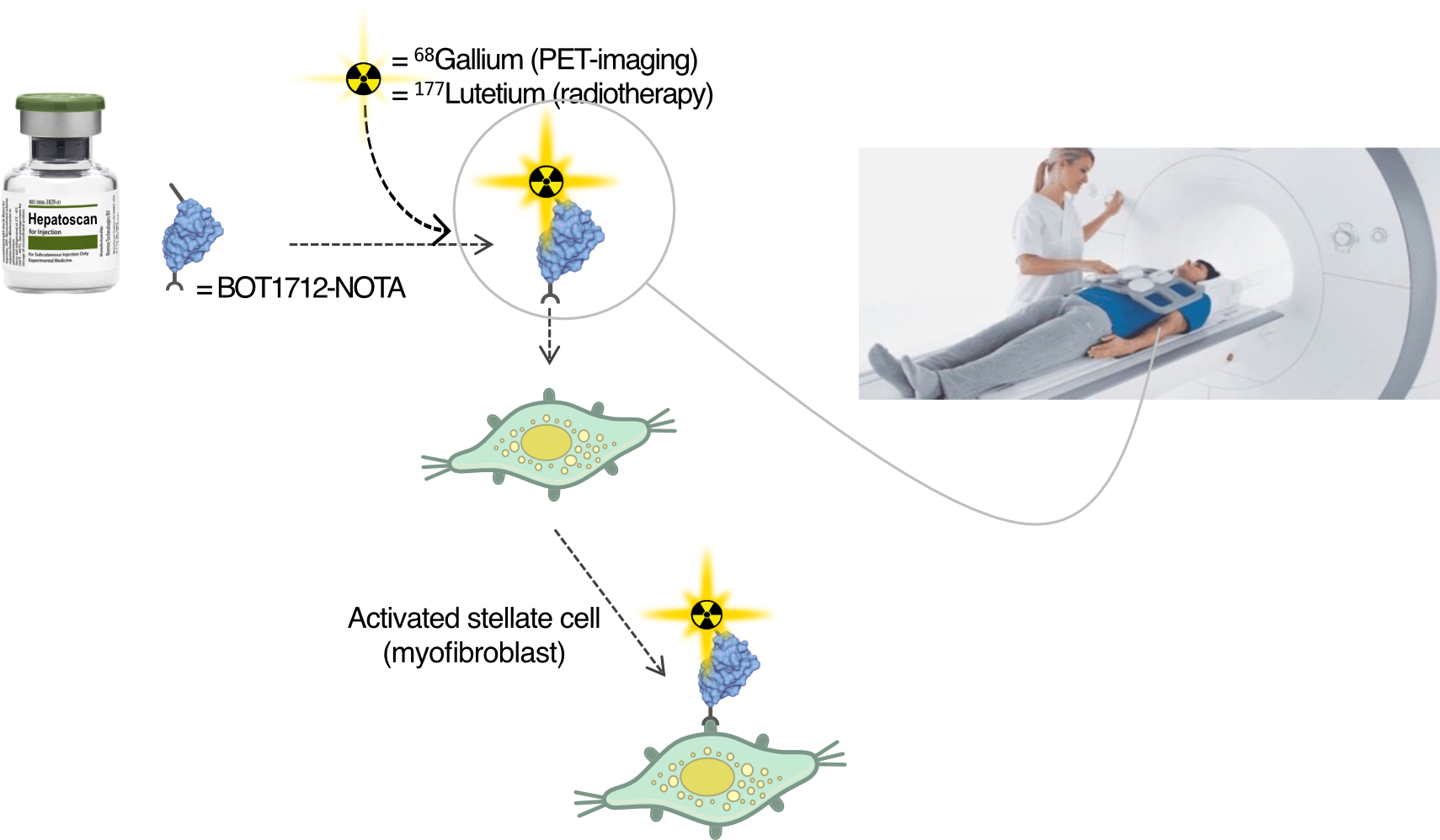
A theranostic is a combination of the terms therapeutic and diagnostic. It is generally used to describe the combination of using one single radiopharmaceutical drug to identify (diagnose) and treat (therapy) a disease, such as a main tumor and any metastases. Often by changing the radionuclide label from a diagnostic radionuclide, such as 68-Gallium or 18-Fluorine, and a therapeitic radionuclide, such 177-Lutetium.
The receptor-binding bicyclic peptide BOT5035 or single domain antibody BOT1712 can be labeled with a PET radionuclide, here Gallium-68, for PET imaging diagnostic purposes. For the colon cancer metastases indication, BOT1712 can be labeled with a radio-toxic radionuclide, here Lutetium-177, causing the receptor-bearing cells to be damaged from radiation and eliminated.
PDGF / PDGFR axis
BiOrion’s core technology of its 2 lead programs is based on proprietary PDGFRB binding bicyclic peptides and binding single domain antibodies.
All the PDGF sub-types are growth factors that regulate recruitment and growth of cells, and, together with TGF-ß, are the main drivers of fibroblast proliferation, trans-differentiation and activation during fibrosis. PDGFRB are specifically overexpressed on myofibroblasts from different sources, including pericytes, as they are present in all fibrotic organs and tissues.
The binding of the bicyclic peptides and single domain antibodies in combination with the cell-specific overexpression of PDGFRB, allow cell specific targeting to myofibroblasts.
BiOrion’s bicyclic peptides and single domain antibodies can be conjugated to functional groups such as NOTA, allowing chelation of radionuclides for PET-imaging diagnostics and targeted radiotherapy, but also (existing) antifibrotic drugs, for antifibrotic therapy. The bicyclic peptide-drug conjugates and single domain antibody-drug conjugates bind to PDGFRB without interfering in the PDGF signaling cascade. Adverse side effects and off-target effects have not be seen and are therefore unlikely. After binding to PDGFRB on myofibroblasts, the bicyclic peptide-drug conjugates and single domain antibody-drug conjugates are internalized and have their intended effect. The PDGFRB is therefore used as a Trojan horse: solely binding to the receptor to get internalized and accumulated into the myofibroblast, without any effect on PDGF signaling.
