Cortalix Nanobody Services
Discover our 6-step services solutions
STEP 4: Genetic Engineering
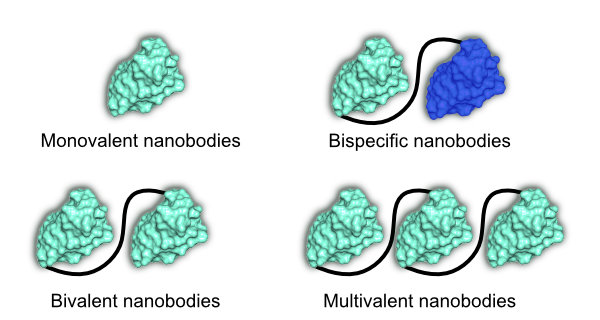
Now that the most effective VHH candidates have been selected based on their antigen binding characteristics, the next step is to construct optimized and engineered VHH sequences to match the application that you have in mind. For example, VHHs can be humanized, and sequence or structural liability sites can be removed to enhance clinical potential. Another option is to construct multivalent nanobodies by placing two or, if necessary, more nanobodies in a row to add new properties to the nanobody. In this way, bispecific nanobodies can be generated that can bind two different epitopes. We can also apply affinity maturation to increase the binding affinity with targeted mutations in the CDRs. Moreover, as described in step 2, a C-terminal tag can be genetically fused to the VHH in order to apply particular purification or detection methods during downstream processing and analysis of the VHH. To generate VHHs that can be conjugated to functional groups, a free (often C-terminal) cysteine will be genetically engineered in the VHH expression construct. There are many possibilities, and we are eager to work together to develop a genetic design tailored to your needs.
What can you expect from step 4
- After intensive consultation, the required VHH variants will be designed in silico followed by the molecular cloning of the genetic constructs in the laboratory.
- Advice on the humanization of VHH sequences and prediction of developability profiles?
- Deliverables:
- Details about the amino acid modifications compared to the basic framework.
- A comprehensive study report
- Expert advice for further development